New Options: `equal_axis`, `transect_slope`, `dark_mode`
All new options are optional and backwards compatible so there should be no impact to existing scripts
equal_axis
Closes: 4 where perpendicular width lines do not appear perpendicular
equal_axis will set the x and y axis of the plot to be equal. Useful to show the perpendicular width lines as perpendicular since it can appear distorted by default in Matplotlib
| equal_axis=False | equal_axis=True |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| 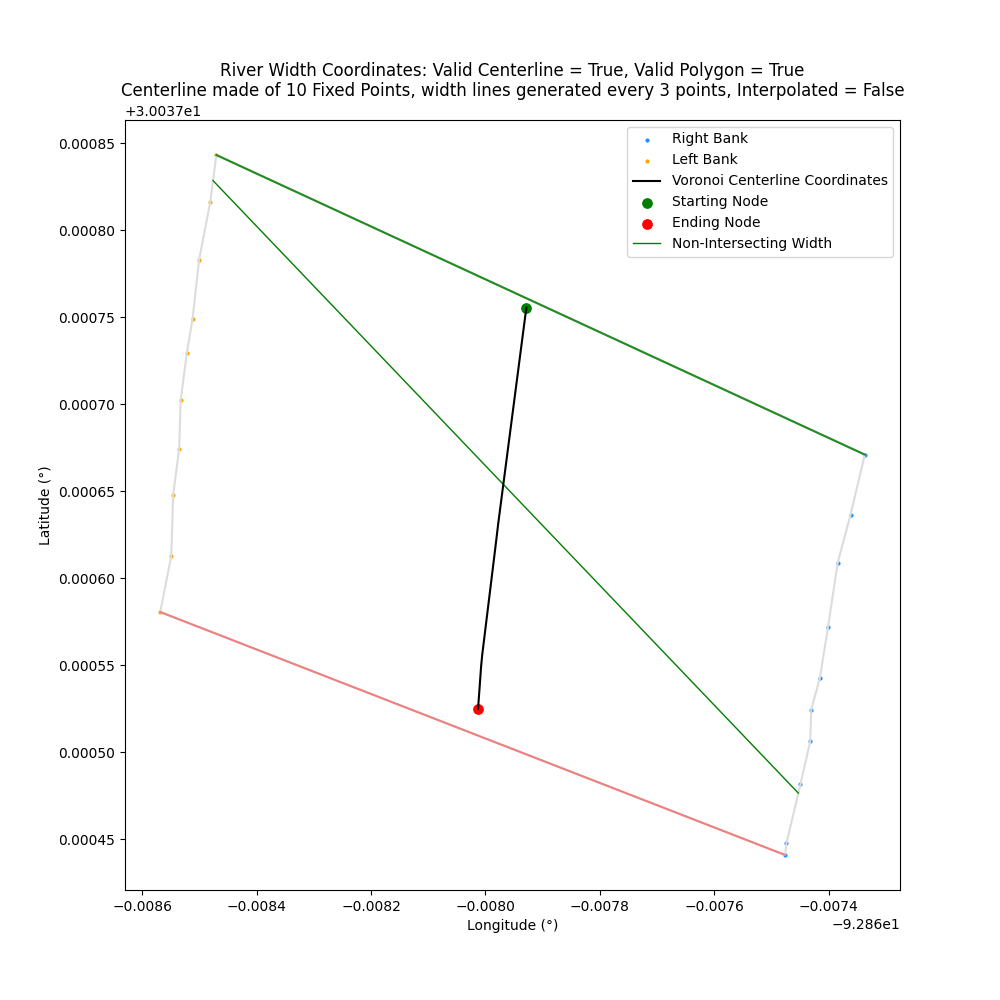 | 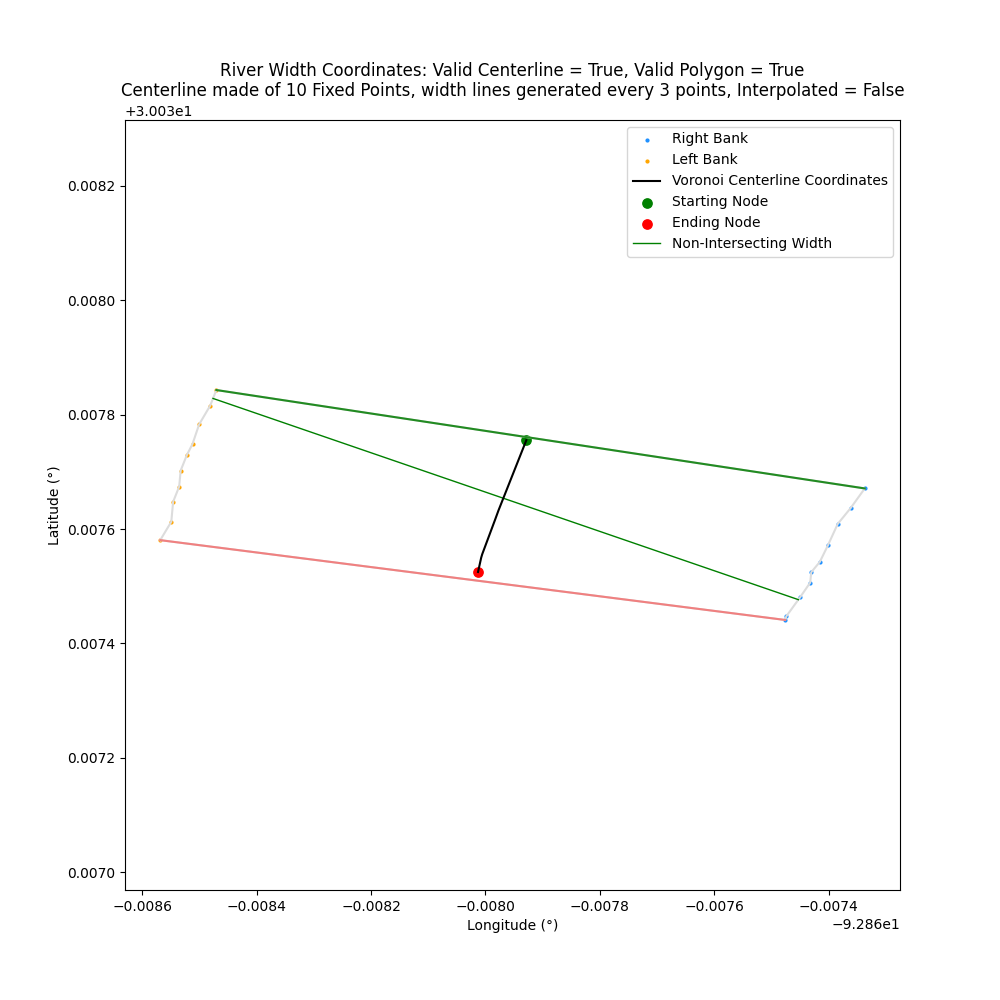|
transect_slope
The width lines are generated as perpendicular to the slopes of the points across `transect_span_distance`
By default, `transect_slope="Average"` where the width lines are perpendicular to the average slopes of the across span distance. For example: `[A, B, C, D] = avg( slope([A, B]) + slope([B, C]) + slope([C+D]) )`
Optionally, if `transect_slope="Direct"` then the width lines will be perpendicular to slope of the first and last point. For example: `[A, B, C, D] = slope([A, D])` to avoid being susceptible to rapid small changes along the centerline
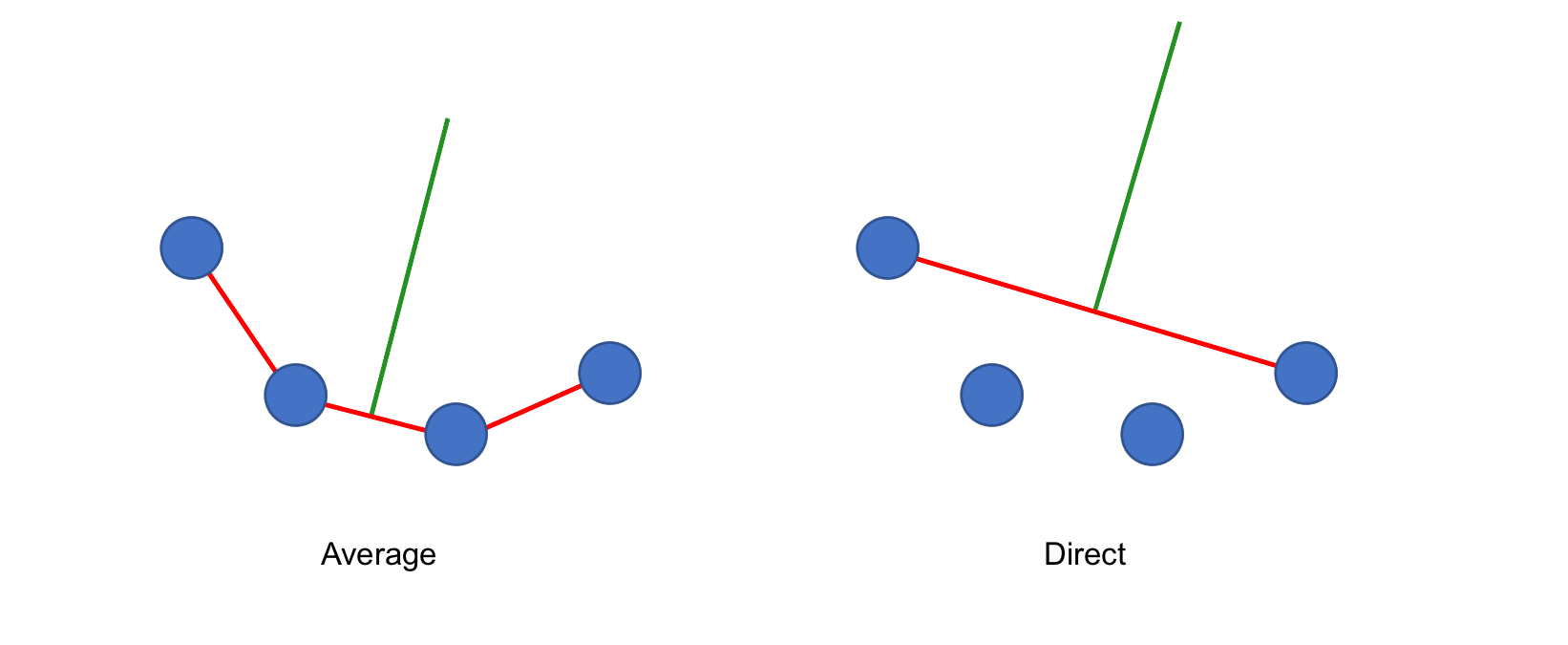
| transect_slope="Average" | transect_slope="Direct" |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| 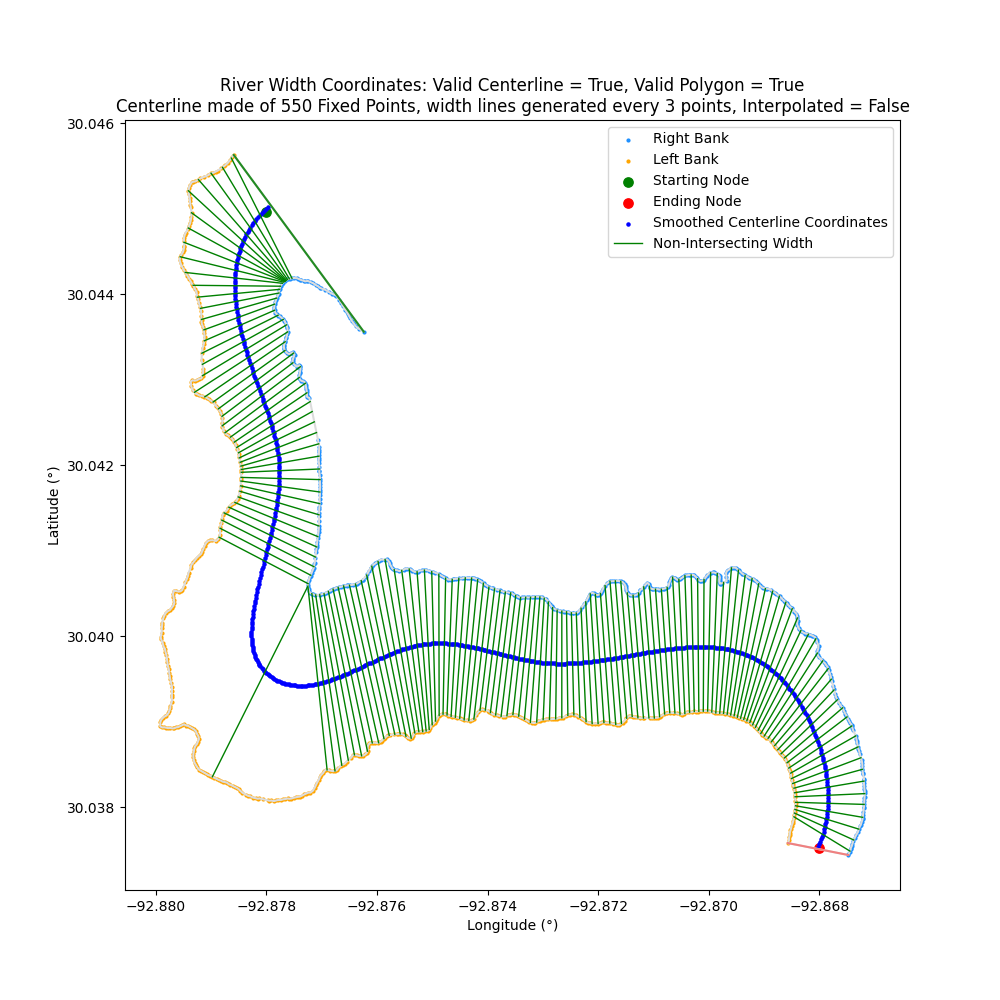 | 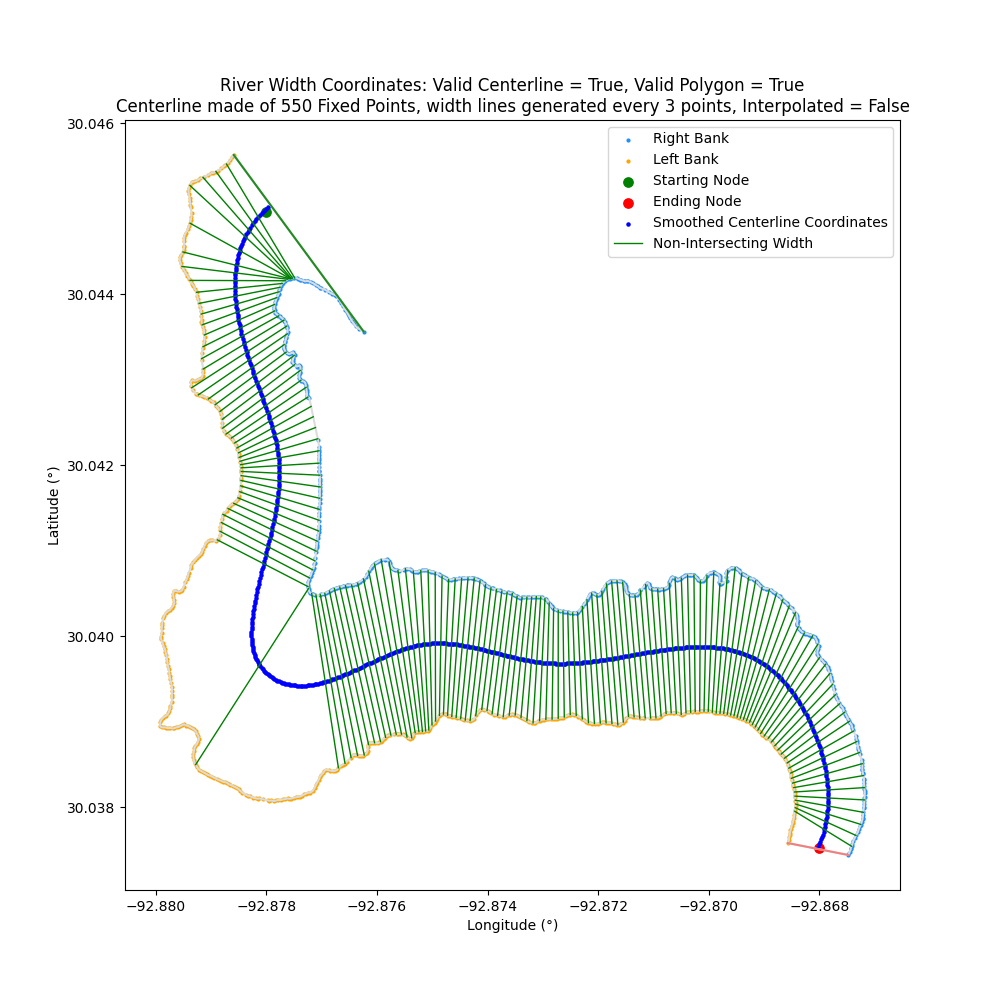 |
dark_mode
New smart dark mode option when generating Matplotlib (for long suffering eyes)
| dark_mode=False | dark_mode=True |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| 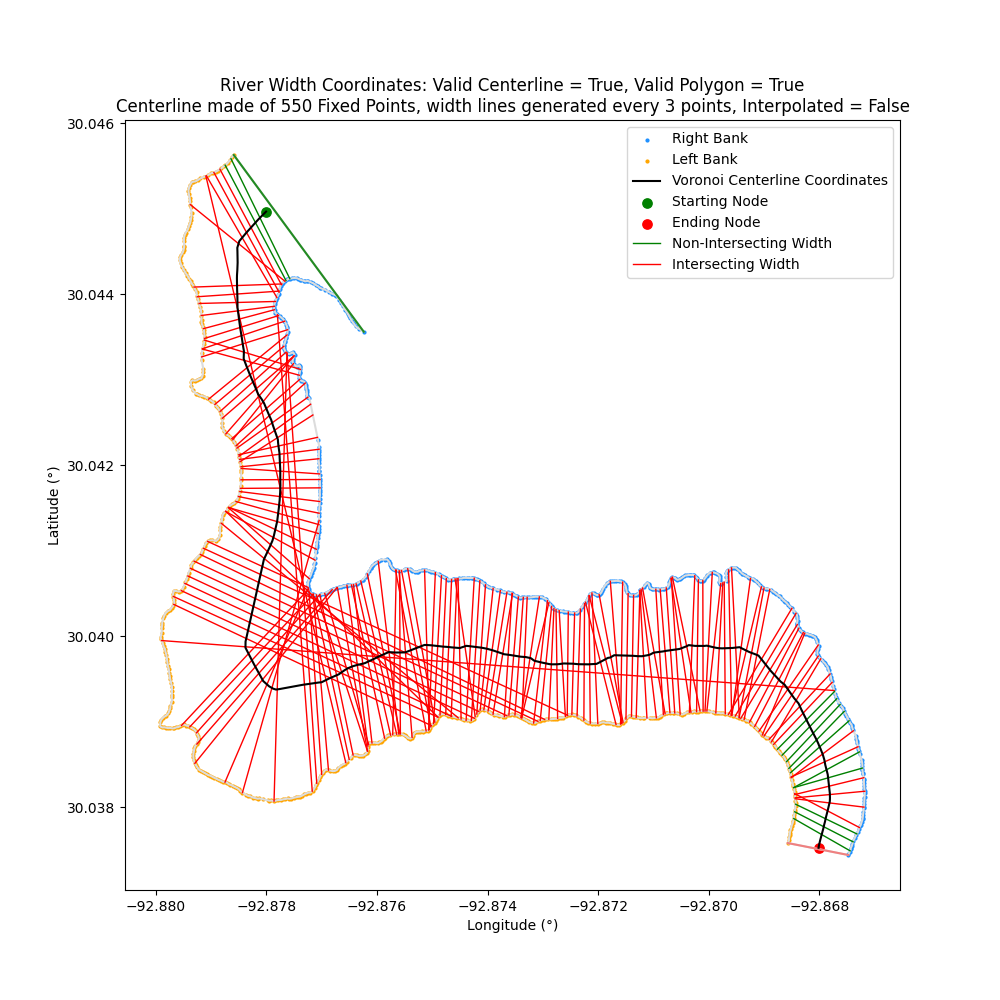 | 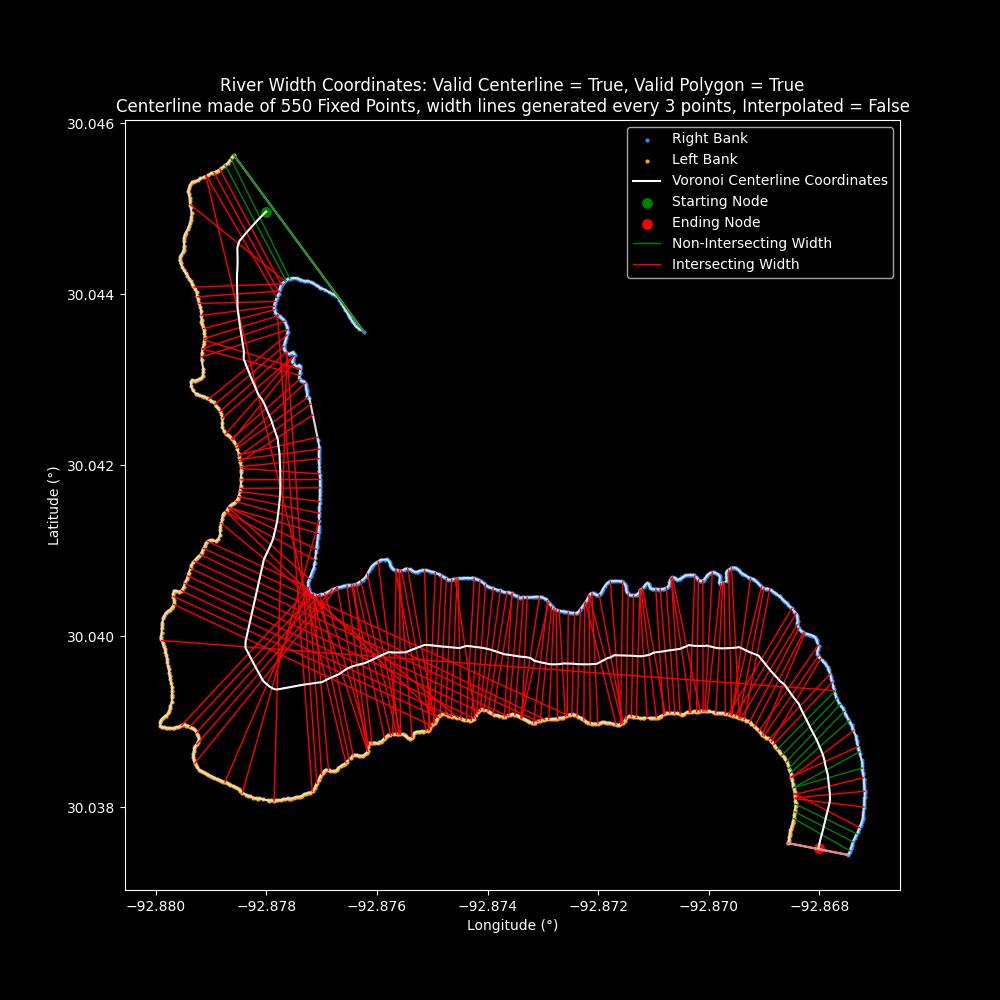|
Additional Changes:
- `transect_span_distance` minimum has been change from 3 to 2 (to measure a single slope)
Note: Re-release of 1.4.0 with hot fix for PyPi package
__Bug fixes and README.md edits__
__Pytests: 229 tests for Python 3.9, 3.10, 3.11__